Industrial borescopes play a vital role in industrial nondestructive testing and are widely used in a wide range of fields, including aerospace, manufacturing, shipbuilding, and energy. When selecting an industrial borescope, in addition to the main unit's functionality, the characteristics of the piping are also crucial, as they impact the safety and accuracy of the inspection. Let's first understand the types of piping used for industrial borescopes.
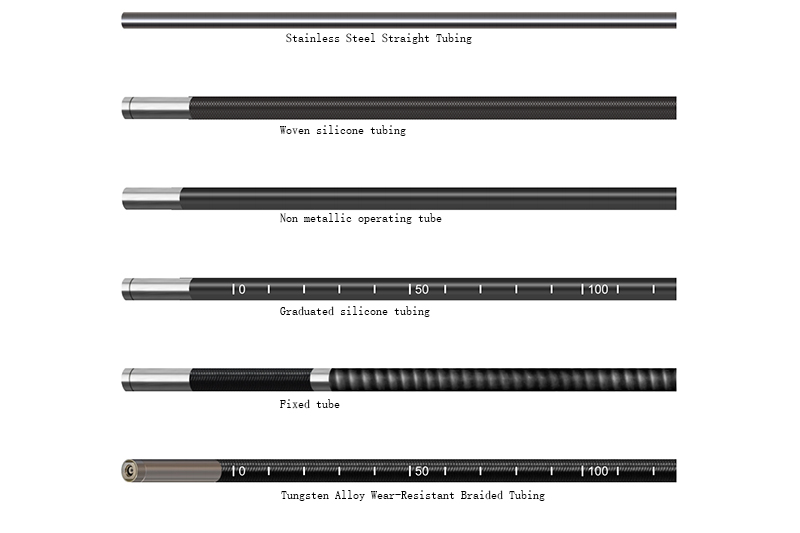
Ⅰ. Analysis of Industrial borescope Piping Types
Industrial borescope piping can be broadly categorized into tungsten alloy wear-resistant braided tubing, stainless steel straight tubing, alloy turbine bend tubing, alloy spring tubing, non-metallic operating tubing, braided silicone tubing, and graduated silicone tubing.
1. Tungsten Alloy Wear-Resistant Braided Tubing: This tubing is based on standard tubing but incorporates a tungsten alloy braided layer on the outer layer, significantly enhancing wear resistance. It offers exceptional wear resistance, exceptional crush resistance, and a long service life. However, this comes at the cost of increased cost, possible weight, and slightly reduced flexibility.
2. Stainless Steel Straight Tubing: The tubing is highly rigid and resists bending. It offers excellent pushability, maintains a straight line, and facilitates access to deep, straight holes. Completely unbendable, suitable only for straight channels.
3. Alloy Turbine Bend: The bend can be fixed after bending. Precise positioning allows for stable viewing of lateral areas (such as cylinder walls and pipe walls). Limited flexibility, allowing only specific angles of bending and turning.
4. Alloy Spring Tube: The support structure is a spring skeleton. It offers excellent flexibility and bendability, while maintaining a certain degree of rigidity to ensure pushability. However, its torque transmission and precise controllability are inferior to those of braided mesh tubing.
5. Non-metallic Operating Tube: Typically, compared to metal operating tubes, the tubing is coated with fiber (Kevlar) or other non-metallic materials. It is insulated, explosion-proof, lightweight, and flexible. However, its wear resistance and torque transmission are inferior to those of tungsten alloy braided tubing.
6. Braided Silicone Tube: Braided tubing with a silicone outer layer. It offers excellent chemical and high temperature resistance (up to 200°C and above), and good biocompatibility. However, its mechanical strength (scratch and tear resistance) is relatively low.
7. Scaled Silicone Tube: Special Features: Based on the silicone tubing, it incorporates distance scales. It can directly measure the depth and location of defects without requiring secondary measurements, making it very practical. However, it shares the same disadvantages as silicone tubing, and the scale may become blurred due to wear.
Ⅱ. How to Select Industrial borescope Tubing Based on the Application Scenario
The key to selection lies in analyzing the "channel environment" and "inspection objectives" of your inspection object. The following scenarios are examples:
Scenario 1: Engines, Hydraulic Systems, Gearboxes - Environment: High wear, heavy oil, and complex bends
Core Challenge: Internally exposed to sharp burrs, metal debris, and curved channels, requiring extremely wear-resistant tubing and precise control.
Preferred Recommendation: Tungsten Alloy Wear-Resistant Braided Tubing.
Reason: Its exceptional wear resistance makes it the best choice for these "harsh environments," minimizing internal scratches, abrasion, and even punctures, extending equipment life. Alloy turbine bends are often used to inspect specific areas such as cylinder walls.
Scenario 2: Power Systems (such as generators and high-voltage switchgear) - Live work and the impact of electronic components
Core Challenge: The risk of electric shock and short circuits must be absolutely prevented. Preferred: Non-metallic operating hose (fiber braided hose, silicone braided hose).
Reason: This is a mandatory safety requirement. If metal hoses come into contact with live parts, they could cause equipment short circuits or electric shock, with disastrous consequences. Industrial borescopes use insulated hoses to effectively prevent such incidents.
Scenario 3: Petrochemical and gas pipelines—flammable and explosive, long distances, and corrosive environments.
Core Challenges: The presence of flammable materials requires explosion protection; the long length of the hose requires lightness and flexibility; and the potential for contact with chemical media.
Preferred: Non-metallic operating hose or braided silicone hose.
Reason: Non-metallic operating hoses meet explosion-proof requirements and are lightweight, flexible, and suitable for long-distance delivery.
Braided silicone hose: If the environment contains highly corrosive chemicals (such as strong acids and alkalis) or high temperatures (such as steam pipes exceeding 100°C), the silicone hose's chemical and high-temperature resistance makes it the preferred choice.
Scenario 4: Straight and Deep Hole Measurement (e.g., deep holes in castings and pipes)—Precise positioning is required.
Core Challenge: The channel is straight, and the exact depth of the defect from the hole opening must be known.
Preferred Recommendation: Graduated Silicone Tubing or Stainless Steel Straight Tubing.
Reason: Graduated Silicone Tubing: It meets the need for curved access and provides direct readings, maximizing efficiency. For example, if a crack is discovered, the position within the pipe can be immediately read as "5.3 meters."
Stainless Steel Straight Tubing: If the channel is completely straight, without any bends, rigid straight tubing offers the best pushability and prevents accidental bending during the process.
Scenario 5: Food and Pharmaceutical Industries—Meeting Hygiene Standards
Core Challenge: Testing equipment must be cleaned and sterilized to prevent product contamination.
Preferred Recommendation: Braided Silicone Tubing or Stainless Steel Straight Rod.
Reason: Silicone is non-toxic, odorless, and biocompatible. Stainless Steel Straight Tubing can be made of food-grade stainless steel, which generally meets FDA and other hygiene standards and is easy to clean and sterilize.
Ⅲ. Summary of the Industrial borescope Tubing Selection Process:
Identify the characteristics of the inspection aperture: Straight inspection apertures can use straight rods; curved inspection apertures subject to high wear can use wear-resistant tungsten alloy braided tubing; long inspection apertures requiring measurement can use graduated tubing.
Identify the environmental characteristics: Electrically charged and explosive environments can use non-metallic operating tubing; highly corrosive or high-temperature environments can use braided silicone tubing.
Identify the inspection target: For sidewall inspections at fixed angles, alloy turbine bend tubing can be used.
Before purchasing an industrial borescope, please provide us with your specific inspection target (photos, drawings) and requirements. We can provide a professional host and tubing configuration plan.